Jsoup代码解读(2):DOM相关对象,jsoupdom
Jsoup代码解读(2):DOM相关对象,jsoupdom
DOM结构相关类
我们先来看看nodes包的类图:
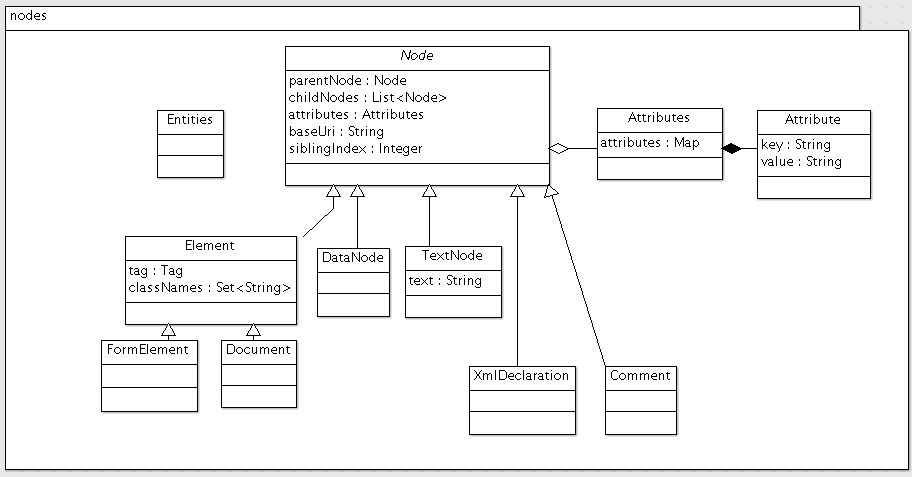
这里可以看到,核心无疑是Node类。
Node类是一个抽象类,它代表DOM树中的一个节点,它包含:
- 父节点
parentNode以及子节点childNodes的引用 - 属性值集合
attributes - 页面的uri
baseUri,用于修正相对地址为绝对地址 - 在兄弟节点中的位置
siblingIndex,用于进行DOM操作
Node里面包含一些获取属性、父子节点、修改元素的方法,其中比较有意思的是absUrl()。我们知道,在很多html页面里,链接会使用相对地址,我们有时会需要将其转变为绝对地址。Jsoup的解决方案是在attr()的参数开始加”abs:”,例如attr(“abs:href”),而absUrl()就是其实现方式。我写的爬虫框架webmagic里也用到了类似功能,当时是自己手写的,看到Jsoup的实现,才发现自己是白费劲了,代码如下:
<!-- lang: java -->
URL base;
try {
try {
base = new URL(baseUri);
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
// the base is unsuitable, but the attribute may be abs on its own, so try that
URL abs = new URL(relUrl);
return abs.toExternalForm();
}
// workaround: java resolves '//path/file + ?foo' to '//path/?foo', not '//path/file?foo' as desired
if (relUrl.startsWith("?"))
relUrl = base.getPath() + relUrl;
// java URL自带的相对路径解析
URL abs = new URL(base, relUrl);
return abs.toExternalForm();
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
return "";
}
Node还有一个比较值得一提的方法是abstract String nodeName(),这个相当于定义了节点的类型名(例如Document是’#Document’,Element则是对应的TagName)。
Element也是一个重要的类,它代表的是一个HTML元素。它包含一个字段tag和classNames。classNames是”class”属性解析出来的集合,因为CSS规范里,”class”属性允许设置多个,并用空格隔开,而在用Selector选择的时候,即使只指定其中一个,也能够选中其中的元素。所以这里就把”class”属性展开了。Element还有选取元素的入口,例如select、getElementByXXX,这些都用到了select包中的内容,这个留到下篇文章select再说。
Document是代表整个文档,它也是一个特殊的Element,即根节点。Document除了Element的内容,还包括一些输出的方法。
Document还有一个属性quirksMode,大致意思是定义处理非标准HTML的几个级别,这个留到以后分析parser的时候再说。
DOM树的遍历
Node还有一些方法,例如outerHtml(),用作节点及文档HTML的输出,用到了树的遍历。在DOM树的遍历上,用到了NodeVisitor和NodeTraversor来对树的进行遍历。NodeVisitor在上一篇文章提到过了,head()和tail()分别是遍历开始和结束时的方法,而NodeTraversor的核心代码如下:
<!-- lang: java -->
public void traverse(Node root) {
Node node = root;
int depth = 0;
//这里对树进行后序(深度优先)遍历
while (node != null) {
//开始遍历node
visitor.head(node, depth);
if (node.childNodeSize() > 0) {
node = node.childNode(0);
depth++;
} else {
//没有下一个兄弟节点,退栈
while (node.nextSibling() == null && depth > 0) {
visitor.tail(node, depth);
node = node.parent();
depth--;
}
//结束遍历
visitor.tail(node, depth);
if (node == root)
break;
node = node.nextSibling();
}
}
}
这里使用循环+回溯来替换掉了我们常用的递归方式,从而避免了栈溢出的风险。
实际上,Jsoup的Selector机制也是基于NodeVisitor来实现的,可以说NodeVisitor是更加底层和灵活的API。
在下一篇博客我会讲讲Document的输出。
本系列:
- Jsoup代码解读(1):概述
- Jsoup代码解读(2):DOM相关对象
用户点评