java集合相关知识(一),
java集合相关知识(一),
一、容器的概念
二、容器API
三、Collection接口
四、Iterator接口
五、Iterable接口
六、Set接口
七、Comparable接口
八、List接口
九、Map接口
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
一、容器的概念
为什么使用集合框架?
如果并不知道程序运行时会需要多少对象,或者需要更复杂方式存储对象----可以使用java集合框架
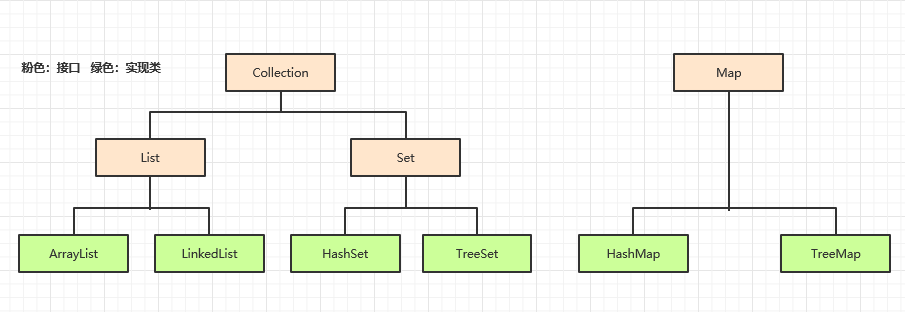
二、Collection接口:存放的是单一值
特点:
1、可以存储不同的数据类型,而数组只能存放固定类型的数据;
2、当使用ArrayList子类实现时,初始化的长度是10,当长度不够的时候会自动进行扩容操作;
api方法:
add:要求必须传入的参数是Object对象,因此当写入基本数据类型时,包含了自动装箱和自动拆箱的过程;
addAll:田间另一个集合的元素到此集合中;
clear:只是清空集合中的元素,但是此集合对象并没有被回收;
remove:删除指定元素;
removeAll:删除集合元素;
contains:判断集合中是否包含指定的元素值;
constainsAll:判断此集合中是否包含另一个集合;
isEmpty:判断集合是否为空;
retainAll:若集合中拥有另一个集合的所有元素,返回true,否则false;
size:返回当前集合的大小;
toArray:将集合转化成数组;
三、List和Set接口:
List特点:有序,不唯一(可重复)
ArrayList和LinkedList区别?
ArrayList是长度可变的数组,在内存中分配连续的空间;
优点:遍历和随机访问元素效率比较高;
缺点:添加和删除需要大量移动元素效率低,按照内容查询效率低;
LinkedList是采用链表存储方式;
优点:添加、删除效率比较高;
缺点:遍历和随机访问元素效率低;
Vector:(面试常问)
1、Vector也是List接口的一个子类实现;
2、 Vector跟ArrayList一样,底层都是使用数组进行实现的;
3、面试经常问区别:
(1)ArrayList是线程不安全的,效率高;Vector是线程安全的,效率低;
(2)ArrayList进行扩容时是扩容1.5倍,Vector进行扩容的时候是扩容2倍;
迭代器Iterator:(需要详细补充+源码解析+图)
循环的方式:
do...while
while
for
还有一种增强for循环的方式,可以简化循环的编写

所有的集合类都默认实现了Iterable的接口,实现此接口意味着具备了增强for循环的能力,也就是for-each
增强for循环本质上使用的也是itertor的功能
方法:
iterator();
foreach();
在iterator的方法中,要求返回一个Iterator的接口子类实例对象,此接口中包含了hasNext() next() remove()(此方法不常用)
iterator和for循环的区别:参考链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/cloud-ken/p/11303084.html
在使用iterator进行迭代的过程中如果使用list.remove删除其中的某个元素会报错,ConcurrentModificationException(并发操作异常),因此
如果遍历的同事需要删除元素,建议使用listIterator()
ListIterator迭代器提供了向前和向后两种遍历方式
始终是通过cursor和lastret的指针来获取元素值及向下的遍历索引;
当使用向前遍历的时候必须要保证指针在迭代器的结尾,否则无法获取结果值
详解:以ArrayList为例
ArrayList.class实现Iterable方法的代码(内部类实现)
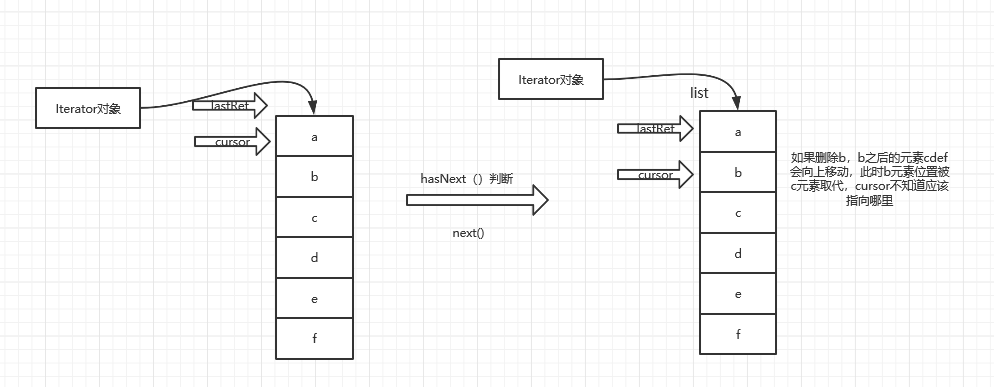

iterator里的remove方法会重新把lastRet赋值给cursor,lastRet=-1,所以不会发生ConcurrentModificationException错误。
相关文章
- 暂无相关文章
用户点评