spring——AOP原理及源码(二),
回顾:
在上一篇中,我们提到@EnableAspectJAutoProxy注解给容器中加入了一个关键组件internalAutoProxyCreator的BeanDefinition,实际类型为
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator的BeanDenation
并且发现这是一个后置处理器,也是一个XXXAware接口的实现类。以及探究了它的继承关系如下。

接下来我们就从后置处理器和BeanFactoryAware的角度来看看AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator的BeanDefinition创建完成后都做了什么。
一、设置调试断点
我们分别进入四个有关类,在类中与后置处理器和BeanFactoryAware有关的方法上打上断点。最终效果如下:
AbstractAutoProxyCreator.setBeanFactory
AbstractAutoProxyCreator有后置处理器逻辑
{
postProcessBeforeInstantiation()
postProcessAfterInitialization()
}
AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator.initBeanFactory
AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator.setBeanFactory
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator.initBeanFactory
最后,在配置类中给两个bean方法打上断点。
二、调试过程
开始调试,我们会发现还是先来到上一篇的AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator的BeanDenation创建过程。
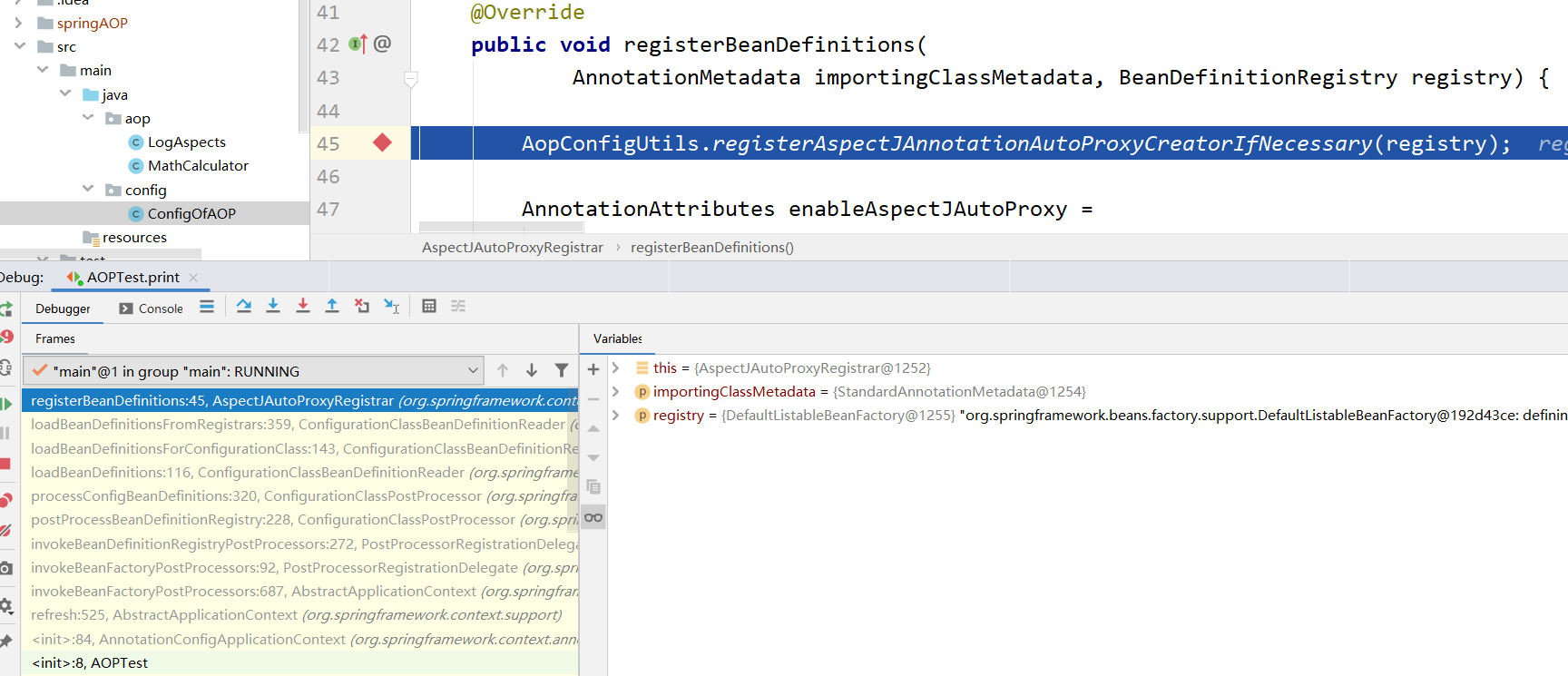
左下角frames框中选到refresh方法可以看到,AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator的BeanDenation的创建是invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors()方法调用来的。
调用这个方法在上下文中生成后置处理器的BeanDefinition加入容器中。
下一步的registerBeanPostProcessors才是注册后置处理器(利用BeanDefinition的信息注册对应Bean),也是本篇的重点。
为了让它快速创建完BeanDefinition,这里我们直接快进到下一个断点。
程序先来到了AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator的setBeanFactory方法
为了从头看起,还是先在frames框中选到refresh方法,可以看到来到了refresh的下一方法,将要开始注册后置处理器。

二点一、registerBeanPostProcessors()
我们继续在frames中往上点,直到来到PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.registerBeanPostProcessors()
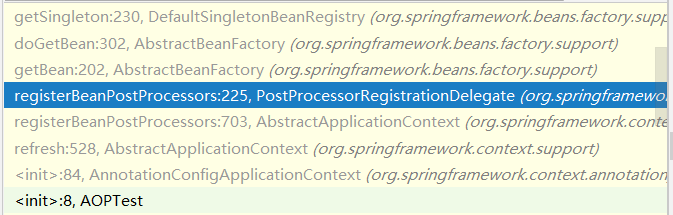
方法有点长,但关键只在其中几个地方,我们将在下面进行针对分析
![]() 1 public static void registerBeanPostProcessors(
2 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, AbstractApplicationContext applicationContext) {
3
4
1 public static void registerBeanPostProcessors(
2 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, AbstractApplicationContext applicationContext) {
3
4 String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanPostProcessor.
class,
true,
false);
5
6 // Register BeanPostProcessorChecker that logs an info message when
7 // a bean is created during BeanPostProcessor instantiation, i.e. when
8 // a bean is not eligible for getting processed by all BeanPostProcessors.
9 int beanProcessorTargetCount = beanFactory.getBeanPostProcessorCount() + 1 +
postProcessorNames.length;
10 beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(
new BeanPostProcessorChecker(beanFactory, beanProcessorTargetCount));
11
12 // Separate between BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,
13 // Ordered, and the rest.
14 List<BeanPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors =
new ArrayList<BeanPostProcessor>
();
15 List<BeanPostProcessor> internalPostProcessors =
new ArrayList<BeanPostProcessor>
();
16 List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames =
new ArrayList<String>
();
17 List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames =
new ArrayList<String>
();
18 for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
19 if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.
class)) {
20 BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.
class);
21 priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
22 if (pp
instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
23 internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
24 }
25 }
26 else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.
class)) {
27 orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
28 }
29 else {
30 nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
31 }
32 }
33
34 // First, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
35 sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
36 registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, priorityOrderedPostProcessors);
37
38 // Next, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
39 List<BeanPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors =
new ArrayList<BeanPostProcessor>
();
40 for (String ppName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
41 BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.
class);
42 orderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
43 if (pp
instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
44 internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
45 }
46 }
47 sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
48 registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors);
49
50 // Now, register all regular BeanPostProcessors.
51 List<BeanPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors =
new ArrayList<BeanPostProcessor>
();
52 for (String ppName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
53 BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.
class);
54 nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
55 if (pp
instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
56 internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
57 }
58 }
59 registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, nonOrderedPostProcessors);
60
61 // Finally, re-register all internal BeanPostProcessors.
62 sortPostProcessors(internalPostProcessors, beanFactory);
63 registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, internalPostProcessors);
64
65 // Re-register post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners,
66 // moving it to the end of the processor chain (for picking up proxies etc).
67 beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(
new ApplicationListenerDetector(applicationContext));
68 }
registerBeanPostProcessors
4:获取所有后置处理器的名字
14~32:对实现不同接口的后置处理器进行分类
35~48:对上面的分类分别进行处理,因为实现的是Ordered接口,我们只关注39~48行
40~46:遍历分好的实现了Ordered接口的后置处理器名,利用beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class)来获取
二点二、doGetBean()
有了以上的步骤,我们主要来看beanFactory是怎么获取的

可以看到,先来到了getBean方法,然后又进入了doGetBean方法。下面我们来看doGetBean做了什么。

![]() 1 /**
2 * Return an instance, which may be shared or independent, of the specified bean.
3 * @param name the name of the bean to retrieve
4 * @param requiredType the required type of the bean to retrieve
5 * @param args arguments to use when creating a bean instance using explicit arguments
6 * (only applied when creating a new instance as opposed to retrieving an existing one)
7 * @param typeCheckOnly whether the instance is obtained for a type check,
8 * not for actual use
9 * @return an instance of the bean
10 * @throws BeansException if the bean could not be created
11 */
12
1 /**
2 * Return an instance, which may be shared or independent, of the specified bean.
3 * @param name the name of the bean to retrieve
4 * @param requiredType the required type of the bean to retrieve
5 * @param args arguments to use when creating a bean instance using explicit arguments
6 * (only applied when creating a new instance as opposed to retrieving an existing one)
7 * @param typeCheckOnly whether the instance is obtained for a type check,
8 * not for actual use
9 * @return an instance of the bean
10 * @throws BeansException if the bean could not be created
11 */
12 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked"
)
13 protected <T>
T doGetBean(
14 final String name,
final Class<T> requiredType,
final Object[] args,
boolean typeCheckOnly)
15 throws BeansException {
16
17 final String beanName =
transformedBeanName(name);
18 Object bean;
19
20 // Eagerly check singleton cache for manually registered singletons.
21 Object sharedInstance =
getSingleton(beanName);
22 if (sharedInstance !=
null && args ==
null) {
23 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
24 if (isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
25 logger.debug("Returning eagerly cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName +
26 "' that is not fully initialized yet - a consequence of a circular reference"
);
27 }
28 else {
29 logger.debug("Returning cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "'"
);
30 }
31 }
32 bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName,
null);
33 }
34
35 else {
36 // Fail if we're already creating this bean instance:
37 // We're assumably within a circular reference.
38 if (isPrototypeCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
39 throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName);
40 }
41
42 // Check if bean definition exists in this factory.
43 BeanFactory parentBeanFactory =
getParentBeanFactory();
44 if (parentBeanFactory !=
null && !
containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) {
45 // Not found -> check parent.
46 String nameToLookup =
originalBeanName(name);
47 if (args !=
null) {
48 // Delegation to parent with explicit args.
49 return (T) parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, args);
50 }
51 else {
52 // No args -> delegate to standard getBean method.
53 return parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, requiredType);
54 }
55 }
56
57 if (!
typeCheckOnly) {
58 markBeanAsCreated(beanName);
59 }
60
61 try {
62 final RootBeanDefinition mbd =
getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
63 checkMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanName, args);
64
65 // Guarantee initialization of beans that the current bean depends on.
66 String[] dependsOn =
mbd.getDependsOn();
67 if (dependsOn !=
null) {
68 for (String dep : dependsOn) {
69 if (isDependent(beanName, dep)) {
70 throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
71 "Circular depends-on relationship between '" + beanName + "' and '" + dep + "'"
);
72 }
73 registerDependentBean(dep, beanName);
74 getBean(dep);
75 }
76 }
77
78 // Create bean instance.
79 if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
80 sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName,
new ObjectFactory<Object>
() {
81 @Override
82 public Object getObject()
throws BeansException {
83 try {
84 return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
85 }
86 catch (BeansException ex) {
87 // Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there
88 // eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution.
89 // Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean.
90 destroySingleton(beanName);
91 throw ex;
92 }
93 }
94 });
95 bean =
getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
96 }
97
98 else if (mbd.isPrototype()) {
99 // It's a prototype -> create a new instance.
100 Object prototypeInstance =
null;
101 try {
102 beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
103 prototypeInstance =
createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
104 }
105 finally {
106 afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
107 }
108 bean =
getObjectForBeanInstance(prototypeInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
109 }
110
111 else {
112 String scopeName =
mbd.getScope();
113 final Scope scope =
this.scopes.get(scopeName);
114 if (scope ==
null) {
115 throw new IllegalStateException("No Scope registered for scope name '" + scopeName + "'"
);
116 }
117 try {
118 Object scopedInstance = scope.get(beanName,
new ObjectFactory<Object>
() {
119 @Override
120 public Object getObject()
throws BeansException {
121 beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
122 try {
123 return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
124 }
125 finally {
126 afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
127 }
128 }
129 });
130 bean =
getObjectForBeanInstance(scopedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
131 }
132 catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
133 throw new BeanCreationException(beanName,
134 "Scope '" + scopeName + "' is not active for the current thread; consider " +
135 "defining a scoped proxy for this bean if you intend to refer to it from a singleton"
,
136 ex);
137 }
138 }
139 }
140 catch (BeansException ex) {
141 cleanupAfterBeanCreationFailure(beanName);
142 throw ex;
143 }
144 }
145
146 // Check if required type matches the type of the actual bean instance.
147 if (requiredType !=
null && bean !=
null && !
requiredType.isInstance(bean)) {
148 try {
149 return getTypeConverter().convertIfNecessary(bean, requiredType);
150 }
151 catch (TypeMismatchException ex) {
152 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
153 logger.debug("Failed to convert bean '" + name + "' to required type '" +
154 ClassUtils.getQualifiedName(requiredType) + "'"
, ex);
155 }
156 throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass());
157 }
158 }
159 return (T) bean;
160 }
AbstractBeanFactory.doGetBean
17:获取后置处理器的名称(这里也就是internalAutoProxyCreator)
21:根据bean名字获取对应单例
22~33:如果获取到的bean不为空,进行一系列操作(这里的internalAutoProxyCreator是第一次获取,bean应该是空,所以我们跳过22~33)
61:getMergedLocalBeanDefinition() 根据传入的后置处理器名称,获取其所有信息,在这里也就是从internalAutoProxyCreator的BeanDefinition中获取必要信息,这是为创建bean做准备。
79:判断如果是单例,调用getSingleton()来获取
这里我们先不急着进入getSingleton()方法,接着往下看先。
130:bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(scopedInstance, name, beanName, mbd) 将79行获取的scopedInstance包装为bean
159:返回bean
ok,getSingleton()的获取是要返回的,所以这步是关键,接下来我们来看看getSingleton()。
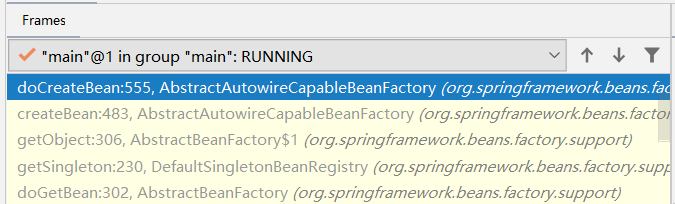
一直往上走,最终我们来到doCreateBean(),说明获取不到,接下来需要创建bean了
二点三、doCreateBean()

![]() 1 /**
2 * Actually create the specified bean. Pre-creation processing has already happened
3 * at this point, e.g. checking {@code postProcessBeforeInstantiation} callbacks.
4 * <p>Differentiates between default bean instantiation, use of a
5 * factory method, and autowiring a constructor.
6 * @param beanName the name of the bean
7 * @param mbd the merged bean definition for the bean
8 * @param args explicit arguments to use for constructor or factory method invocation
9 * @return a new instance of the bean
10 * @throws BeanCreationException if the bean could not be created
11 * @see #instantiateBean
12 * @see #instantiateUsingFactoryMethod
13 * @see #autowireConstructor
14 */
15 protected
1 /**
2 * Actually create the specified bean. Pre-creation processing has already happened
3 * at this point, e.g. checking {@code postProcessBeforeInstantiation} callbacks.
4 * <p>Differentiates between default bean instantiation, use of a
5 * factory method, and autowiring a constructor.
6 * @param beanName the name of the bean
7 * @param mbd the merged bean definition for the bean
8 * @param args explicit arguments to use for constructor or factory method invocation
9 * @return a new instance of the bean
10 * @throws BeanCreationException if the bean could not be created
11 * @see #instantiateBean
12 * @see #instantiateUsingFactoryMethod
13 * @see #autowireConstructor
14 */
15 protected Object doCreateBean(
final String beanName,
final RootBeanDefinition mbd,
final Object[] args)
16 throws BeanCreationException {
17
18 // Instantiate the bean.
19 BeanWrapper instanceWrapper =
null;
20 if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
21 instanceWrapper =
this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
22 }
23 if (instanceWrapper ==
null) {
24 instanceWrapper =
createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
25 }
26 final Object bean = (instanceWrapper !=
null ? instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance() :
null);
27 Class<?> beanType = (instanceWrapper !=
null ? instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass() :
null);
28 mbd.resolvedTargetType =
beanType;
29
30 // Allow post-processors to modify the merged bean definition.
31 synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) {
32 if (!
mbd.postProcessed) {
33 try {
34 applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName);
35 }
36 catch (Throwable ex) {
37 throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
38 "Post-processing of merged bean definition failed"
, ex);
39 }
40 mbd.postProcessed =
true;
41 }
42 }
43
44 // Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references
45 // even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware.
46 boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() &&
this.allowCircularReferences &&
47 isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
48 if (earlySingletonExposure) {
49 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
50 logger.debug("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName +
51 "' to allow for resolving potential circular references"
);
52 }
53 addSingletonFactory(beanName,
new ObjectFactory<Object>
() {
54 @Override
55 public Object getObject()
throws BeansException {
56 return getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean);
57 }
58 });
59 }
60
61 // Initialize the bean instance.
62 Object exposedObject =
bean;
63 try {
64 populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
65 if (exposedObject !=
null) {
66 exposedObject =
initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
67 }
68 }
69 catch (Throwable ex) {
70 if (ex
instanceof BeanCreationException &&
beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) {
71 throw (BeanCreationException) ex;
72 }
73 else {
74 throw new BeanCreationException(
75 mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed"
, ex);
76 }
77 }
78
79 if (earlySingletonExposure) {
80 Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName,
false);
81 if (earlySingletonReference !=
null) {
82 if (exposedObject ==
bean) {
83 exposedObject =
earlySingletonReference;
84 }
85 else if (!
this.allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping &&
hasDependentBean(beanName)) {
86 String[] dependentBeans =
getDependentBeans(beanName);
87 Set<String> actualDependentBeans =
new LinkedHashSet<String>
(dependentBeans.length);
88 for (String dependentBean : dependentBeans) {
89 if (!
removeSingletonIfCreatedForTypeCheckOnly(dependentBean)) {
90 actualDependentBeans.add(dependentBean);
91 }
92 }
93 if (!
actualDependentBeans.isEmpty()) {
94 throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName,
95 "Bean with name '" + beanName + "' has been injected into other beans [" +
96 StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(actualDependentBeans) +
97 "] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been " +
98 "wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the " +
99 "bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using " +
100 "'getBeanNamesOfType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example."
);
101 }
102 }
103 }
104 }
105
106 // Register bean as disposable.
107 try {
108 registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);
109 }
110 catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
111 throw new BeanCreationException(
112 mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature"
, ex);
113 }
114
115 return exposedObject;
116 }
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.doCreateBean
26:创建bean
64:populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper) 给bean的属性赋值
66:initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd)初始化bean
下面我们来看这个初始化bean都做了什么
二点四、initializeBean()

![]() 1 /**
2 * Initialize the given bean instance, applying factory callbacks
3 * as well as init methods and bean post processors.
4 * <p>Called from {@link #createBean} for traditionally defined beans,
5 * and from {@link #initializeBean} for existing bean instances.
6 * @param beanName the bean name in the factory (for debugging purposes)
7 * @param bean the new bean instance we may need to initialize
8 * @param mbd the bean definition that the bean was created with
9 * (can also be {@code null}, if given an existing bean instance)
10 * @return the initialized bean instance (potentially wrapped)
11 * @see BeanNameAware
12 * @see BeanClassLoaderAware
13 * @see BeanFactoryAware
14 * @see #applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization
15 * @see #invokeInitMethods
16 * @see #applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization
17 */
18 protected
1 /**
2 * Initialize the given bean instance, applying factory callbacks
3 * as well as init methods and bean post processors.
4 * <p>Called from {@link #createBean} for traditionally defined beans,
5 * and from {@link #initializeBean} for existing bean instances.
6 * @param beanName the bean name in the factory (for debugging purposes)
7 * @param bean the new bean instance we may need to initialize
8 * @param mbd the bean definition that the bean was created with
9 * (can also be {@code null}, if given an existing bean instance)
10 * @return the initialized bean instance (potentially wrapped)
11 * @see BeanNameAware
12 * @see BeanClassLoaderAware
13 * @see BeanFactoryAware
14 * @see #applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization
15 * @see #invokeInitMethods
16 * @see #applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization
17 */
18 protected Object initializeBean(
final String beanName,
final Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
19 if (System.getSecurityManager() !=
null) {
20 AccessController.doPrivileged(
new PrivilegedAction<Object>
() {
21 @Override
22 public Object run() {
23 invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
24 return null;
25 }
26 }, getAccessControlContext());
27 }
28 else {
29 invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
30 }
31
32 Object wrappedBean =
bean;
33 if (mbd ==
null || !
mbd.isSynthetic()) {
34 wrappedBean =
applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
35 }
36
37 try {
38 invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
39 }
40 catch (Throwable ex) {
41 throw new BeanCreationException(
42 (mbd !=
null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() :
null),
43 beanName, "Invocation of init method failed"
, ex);
44 }
45
46 if (mbd ==
null || !
mbd.isSynthetic()) {
47 wrappedBean =
applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
48 }
49 return wrappedBean;
50 }
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.initializeBean
一进来我们是停在29行的invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean),这里先不看它
我们来关注一下initializeBean的几个重要流程
1、invokeAwareMethods
2、34行applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization
3、38行invokeInitMethods
4、47行applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization
先执行invokeAwareMethods,调用那些XXXAware方法,然后执行后置处理器的applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization方法,接着执行初始化方法,最后执行后置处理器的applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization方法,这也是我们的后置处理器为什么能在bean初始化前后调用方法的原因了。
现在我们往下进入invokeAwareMethods

![]() 1 private void
1 private void invokeAwareMethods(
final String beanName,
final Object bean) {
2 if (bean
instanceof Aware) {
3 if (bean
instanceof BeanNameAware) {
4 ((BeanNameAware) bean).setBeanName(beanName);
5 }
6 if (bean
instanceof BeanClassLoaderAware) {
7 ((BeanClassLoaderAware) bean).setBeanClassLoader(getBeanClassLoader());
8 }
9 if (bean
instanceof BeanFactoryAware) {
10 ((BeanFactoryAware) bean).setBeanFactory(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.
this);
11 }
12 }
13 }
invokeAwareMethods
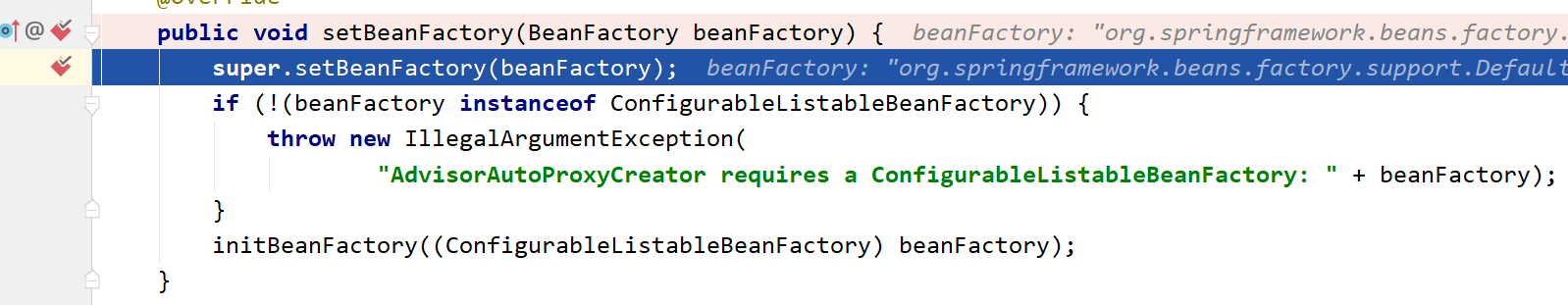
invokeAwareMethods方法先判断是哪个类型的Aware接口,然后调用对应的set方法,所以它最终来到了我们的断点,setBeanFactory()方法
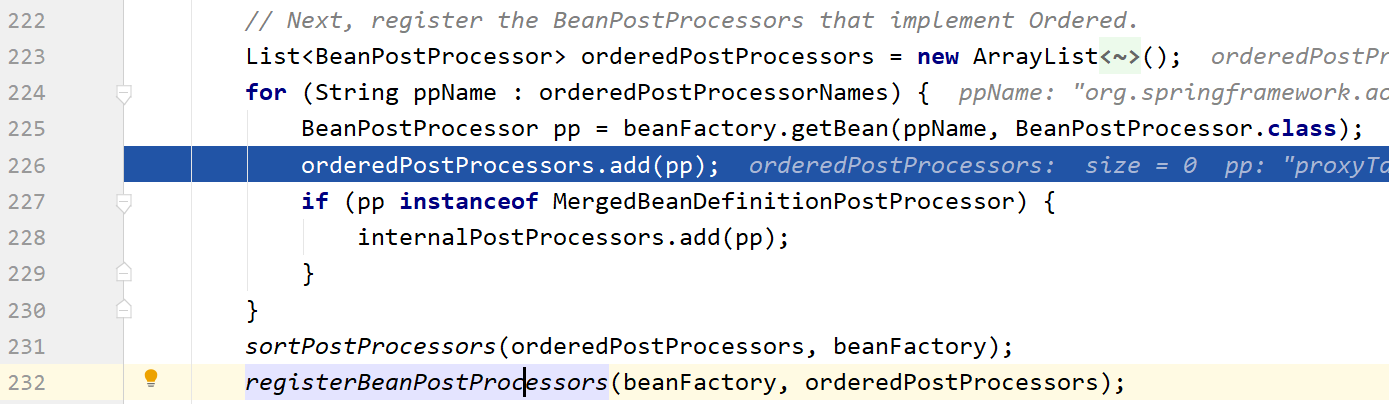
接下来我们一路点击下一步,直到下图,这个BeanPostProcessor就创建完了,并通过orderedPostProcessors.add(pp)先添加到orderedPostProcessors中
再通过registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors)添加到beanFactory中
总结
以上整个过程,是创建完AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator后置处理器bean并存入beanFactory的过程。
下一篇将来探寻AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator在作为后置处理器存入bean工程之后的事。
今天是悲伤,再见了爱人,





![]()












用户点评